Introduction
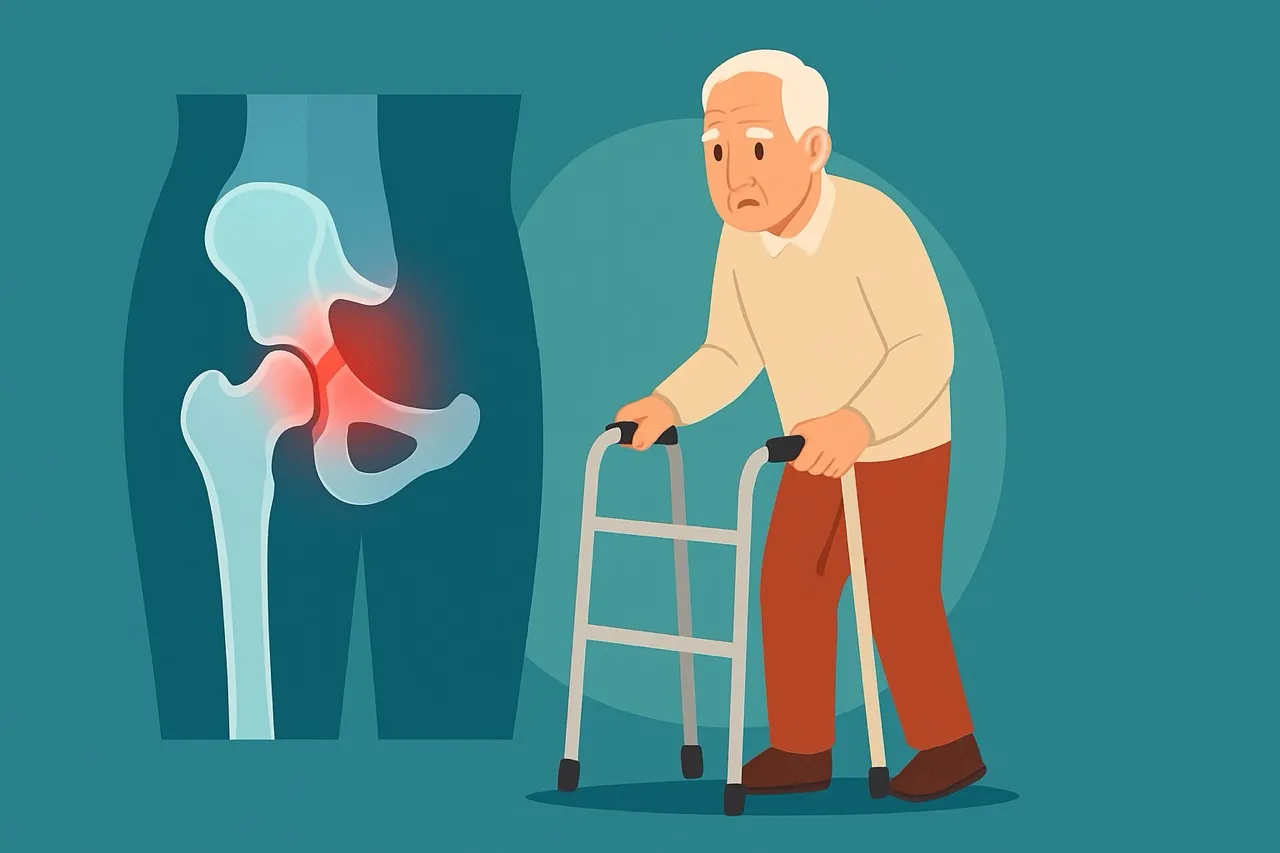
You’re visiting your grandmother one Sunday afternoon. She tries to get up from her chair, slips on the edge of a rug, and lands on the floor. At first, it seems like just a bad fall. But then… she cannot stand. The pain in her hip is sharp. Fear sets in.
For many families, this is not just a story; it’s a reality. It’s a reality. Hip fractures are among the most common and serious injuries in older adults. Especially after the age of 80, even a small fall can lead to a major fracture.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know. From what hip fractures are, to why they happen, to how they are treated, and what recovery looks like. We’ll also cover caregiver tips and prevention strategies.
What is a Hip Fracture in Elderly?
A hip fracture means a break in the upper part of the thigh bone, near the hip joint. Think of the hip joint like a ball sitting in a cup. The “ball” is the top of the thigh bone. When it cracks, we call it a hip fracture.
Why is this such a significant issue for elderly people?
Because with age, bones lose density. They become more fragile, like old wood compared to fresh timber. A fall that might only bruise a younger person can completely break an older person’s hip.
There are different types:
- Femoral neck fracture – a break occurs just below the ball of the hip joint.
- Intertrochanteric fracture – the break happens a little lower down.
- Subtrochanteric fracture – even further down the thigh bone.
All of them are serious. All of them affect mobility.
And here’s the key: hip fractures are not just about bones. They affect the whole person – physically, emotionally, and socially.
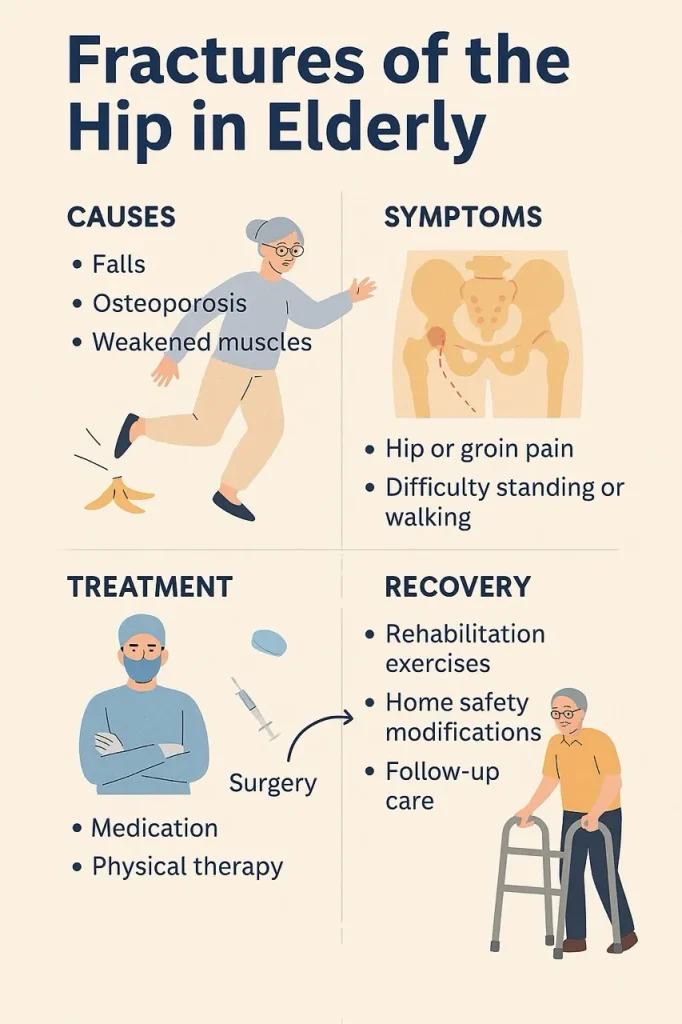
Causes of Hip Fractures in Old Age
Why do elderly people break their hips so easily?
1. Osteoporosis. This is the biggest culprit. Bones lose calcium and become weak. They’re like chalk. One wrong step, and they snap.
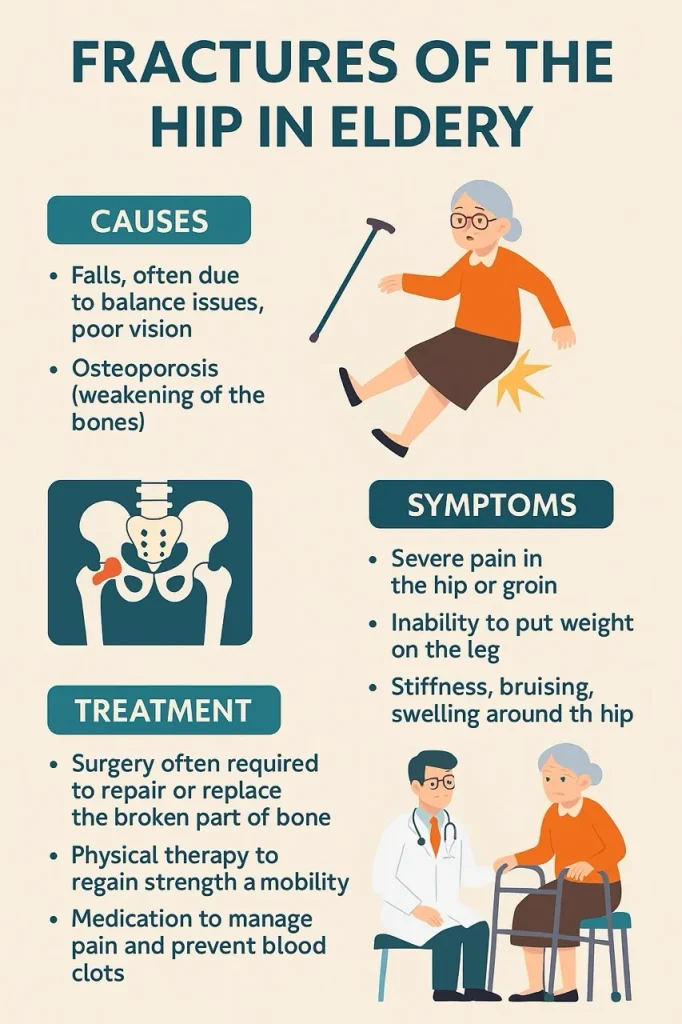
2. Falls. The most common cause. Slipping on wet floors, tripping on rugs, or even losing balance while turning too quickly.
3. Medications. Some drugs cause dizziness. Others affect blood pressure, making seniors prone to falls.
4. Muscle weakness. With age, muscles shrink. They don’t stabilise joints as well.
5. Poor vision. Harder to spot obstacles.
6. Chronic illnesses. Diabetes, arthritis, or neurological problems increase the risk.
When I spoke with an elderly neighbour recently, she told me she avoided going out at night because of poor street lighting. She feared falling more than anything else. That fear is very real in old age.
Symptoms of Hip Fracture in Elderly
How do you know if it’s a hip fracture? Here are the tell-tale signs:
- Severe pain in the hip or groin.
- Inability to walk or put weight on the leg.
- The leg looks shortened or turned outward.
- Swelling or bruising around the hip.
- Sharp pain when moving the leg.
But here’s a surprising fact: sometimes you can fracture your hip and not know it immediately.
Sounds strange. But it happens. A small crack (stress fracture) may only cause mild pain at first. The person might think it’s just arthritis or a pulled muscle. Over time, the crack worsens until walking becomes impossible.
That’s why it’s always safer to check. If an older person complains of hip pain after even a minor fall, don’t ignore it.
Types of Hip Fractures & Treatment Options
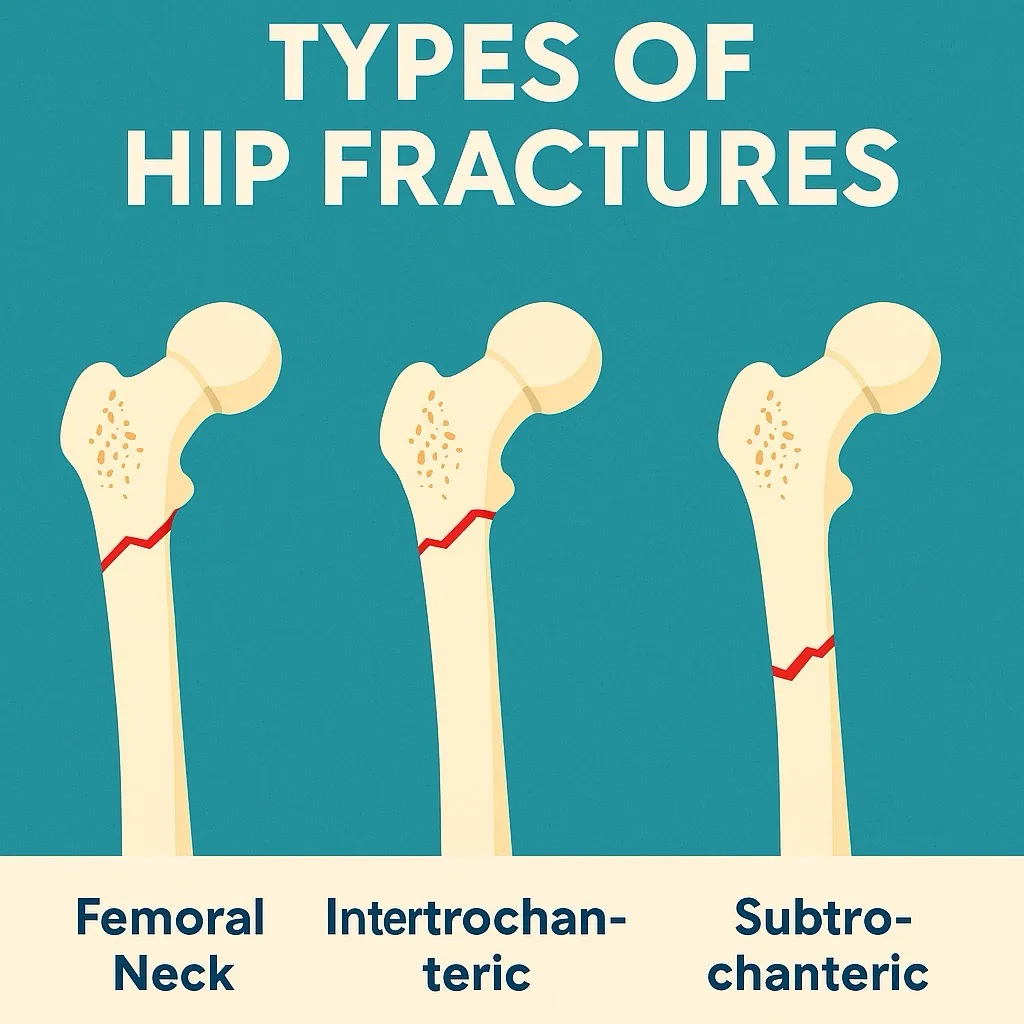
Description: Break just below the ball of the hip joint.
Typical Treatment: Partial or total hip replacement is common due to limited blood supply.
Recovery notes: Progress can be slower. Watch for avascular necrosis and discuss loading limits with the care team.
Description: Break between the neck and shaft of the femur.
Typical Treatment: Internal fixation using screws, a dynamic hip screw, or an intramedullary nail.
- Often heals well due to better blood supply.
- Early mobilization with a walker is common.
Description: Break just below the lesser trochanter.
Typical Treatment: Long intramedullary nail or plate constructs to counter strong muscle forces.
Recovery can be demanding. Physiotherapy focuses on controlled weight bearing and hip abductor strength.
Complications of a Broken Hip in the Elderly
This is where things get really serious.
When a young person breaks a bone, they usually heal. For elderly people, the story is different. Hip fractures can trigger a chain reaction of health problems.
- Immobility. Staying in bed leads to muscle wasting.
- Bed sores. Lying too long in one position. Painful, and can get infected.
- Blood clots. Due to reduced movement. These clots can travel to the lungs.
- Pneumonia. Weak lungs plus long bed rest is a dangerous mix.
- Infections. Especially if surgery is done.
Here’s a hard truth: studies show that life expectancy often drops after a hip fracture in elderly people. Not because of the fracture itself, but because of these complications.
Families often describe it as “the fall that changed everything.”
Treatment Options for Hip Fractures in Elderly
So, what happens after a hip fracture?
Treatment depends on the type of fracture, the patient’s health, and their age.
Surgery for Hip Fracture
Most elderly patients will need surgery. Why? Surgery is necessary as it expedites the restoration of mobility. Without it, they may remain bedridden.
- Hip replacement – the damaged part of the hip is replaced with an artificial joint.
- Internal fixation – screws, plates, or rods are used to hold the bone together.
Doctors decide based on the fracture type. For example, a femoral neck fracture often requires replacement.
Non-Surgical Management
Sometimes, surgery is not possible. If the patient has very poor health or multiple medical issues, doctors may suggest non-surgical care. That means pain relief, physiotherapy, and bed rest. But recovery is much harder this way.
Rehabilitation & Recovery
This is where the real work begins. After surgery, patients need:
- Physiotherapy to regain strength.
- Mobility training: learn to walk with a walker or cane.
- Occupational therapy to adjust daily living activities.
Recovery takes time. For some weeks. Others may need several months to recover.
Recovery and Life After Hip Fracture
What does life look like after a hip fracture?
For many elderly people, it’s a tough road. The body heals slowly after 70 or 80.
- The average recovery timeline is 6–12 months.
- Some regain independence. Others may always need walking support.
- Sadly, some never walk the same way again.
I remember my aunt’s journey. She broke her hip at 82. After surgery, she spent three weeks in the hospital. Then three months in rehab. She learned to walk again, but always needed a cane afterwards. For her, the hardest part was not the pain. It was the loss of independence.
That’s the emotional side of recovery. Fractures don’t just break bones. They break routines, confidence, and sometimes spirits.
Family support makes all the difference here.
Prevention of Hip Fractures in Old Age
Can hip fractures be prevented? Not always. But risks can be reduced.
- Fall-proof the home. Remove loose rugs. Install grab bars in bathrooms. Keep floors dry.
- Improve bone health: calcium, vitamin D, and regular checkups.
- Exercise regularly. Even light walking or yoga strengthens bones and balance.
- Check medications. Review with a doctor if drugs cause dizziness.
- Better vision. Regular eye exams can help prevent tripping hazards.
Think of prevention like putting a safety net under a trapeze artist. You can’t always stop the fall. But you can reduce the damage.
Tips for Caregivers of Elderly with Hip Fracture

Caregiving after a hip fracture is not simple. It demands patience and planning.
- Offer emotional support. Many elderly patients feel depressed after losing mobility.
- Monitor health. Watch for fever, swelling, or breathing issues after surgery.
- Keep them active. Encourage small movements. Even sitting up helps.
- Safety at home. Rearrange furniture to make walking easier.
- Coordinate care. Work with physiotherapists and doctors.
A caregiver once told me, “After my mother’s hip fracture, I became her legs for a while. But in the process, I also became her cheerleader.”
That’s precisely what families need to do.
Conclusion
A broken hip in an elderly person is more than just an injury. It’s a turning point. For some, it marks the beginning of a long recovery. For others, it becomes a permanent change in how they live.
But with the right treatment, strong family support, and careful prevention, many seniors can regain independence.
If you take away one thing from this guide, let it be this: never ignore a fall in an elderly person. Even if they insist they’re fine. Sometimes the damage hides under the surface.
Early action can make the difference between months of suffering and a chance at recovery.
With years of experience in Ilizarov and limb reconstruction techniques, Dr. Ahuja ensures patients have clear timelines, close monitoring, and personalized recovery plans. His focus is not just on bone healing but also on helping patients regain full function and confidence. With guidance from Dr. Divya Ahuja, patients in Thane, Mumbai, and Navi Mumbai receive world-class treatment and full support throughout their journey.
Our Clinical Locations
Tap a location to view timings, contact, and map.
Broadway Healthcare, Dadar East
Broadway Healthcare, Dadar East
Clinic Info
- 📍 Broadway Healthcare, Dadar East, Mumbai
- 🕒 Wednesdays · 10:00 AM – 12:00 NOON
- 📞 Appointments: +91 93213 17227
Sweet Clinics, Vashi, Navi Mumbai
Sweet Clinics, Vashi, Navi Mumbai
Clinic Info
- 📍 Sweet Clinics, Vashi, Navi Mumbai
- 🕒 Fridays · 10:00 AM – 12:00 NOON
- 📞 Appointments: +91 93213 17227
Heal Well Speciality Clinic, Thane West
Heal Well Speciality Clinic, Thane West
Clinic & OPD Info
- 📍 Heal Well Speciality Clinic, Thane West
- 🕒 Every Wednesday 10:00 AM – 11:00 AM
- 📞 Appointments: +91 81691 04438
Mangal Anand Hospital, Chembur Mumbai
Mangal Anand Hospital, Chembur Mumbai
Clinic & OPD Info
- 📍 Mangal Anand Hospital, Chembur Mumbai
- 🕒 Monday, Wednesday, Friday 03-07 PM, Thursday 06-07 PM, Free OPD Saturday 02-04 PM
- 📞 Appointments: +91 70212 18182
SRV Hospitals, Tilaknagar, Chembur
SRV Hospitals, Tilaknagar, Chembur
Clinic Info
- 📍 SRV Hospitals, Tilaknagar, Chembur
- 🕒 Monday, Wednesday, Friday 11 AM-12 PM
- 📞 Appointments: +91 84518 00800
FAQs
How is a fractured hip treated in the elderly?
Most elderly patients with a fractured hip are treated with surgery, either by fixing the bone with screws and plates or replacing part or all of the hip joint. Surgery is usually done within 48 hours for the best outcome. After that, physical therapy and rehabilitation are started quickly to help regain mobility and reduce complications.
What is the first line of imaging for a hip fracture?
The first-line imaging test for a suspected hip fracture is an X-ray. It usually shows the break clearly. If the X-ray looks normal but symptoms suggest a fracture, an MRI or CT scan is done to detect hidden fractures.
What are the big 6 for hip fracture?
The “big 6” refers to key priorities in hip fracture care: pain control, early surgery (within 48 hours), prevention of blood clots, managing medical conditions, early mobilization with physiotherapy, and coordinated geriatric care. Together, these steps improve survival and recovery.
What is a grade 4 hip fracture?
A grade 4 hip fracture usually means a completely displaced fracture where the broken bone ends are no longer aligned. This is often called a displaced femoral neck fracture. It typically requires surgery, often hip replacement, especially in older adults.
What is the protocol for a fractured hip?
The protocol usually involves quick pain relief, urgent imaging (X-ray), stabilization, and surgery within 36–48 hours. After surgery, early mobilization, physiotherapy, and prevention of complications like clots and infections are critical. Multidisciplinary care with both orthopedic and geriatric teams is recommended.
What is the most serious complication of a hip fracture?
The most serious complication is an increased risk of death within the first year, often due to immobility-related problems like pneumonia, blood clots, or infections. Other major concerns are permanent loss of independence and long-term disability.
Can an elderly person survive a broken hip?
Yes. Many do. But survival depends on age, health, and timely treatment.
Can you fracture your hip and not feel pain?
Yes. Small fractures may cause only mild discomfort at first. They often worsen with time.
How long does it take to recover after hip surgery?
Basic walking may resume in 6 to 12 weeks. Full recovery often takes 6 months or more.
Is hip surgery safe after 80?
Yes, but it carries risks. Still, surgery is usually safer than leaving the fracture untreated.
Will they be able to walk again?
Most patients can walk again, though many need walking aids. The outcome depends on health, rehab, and support.