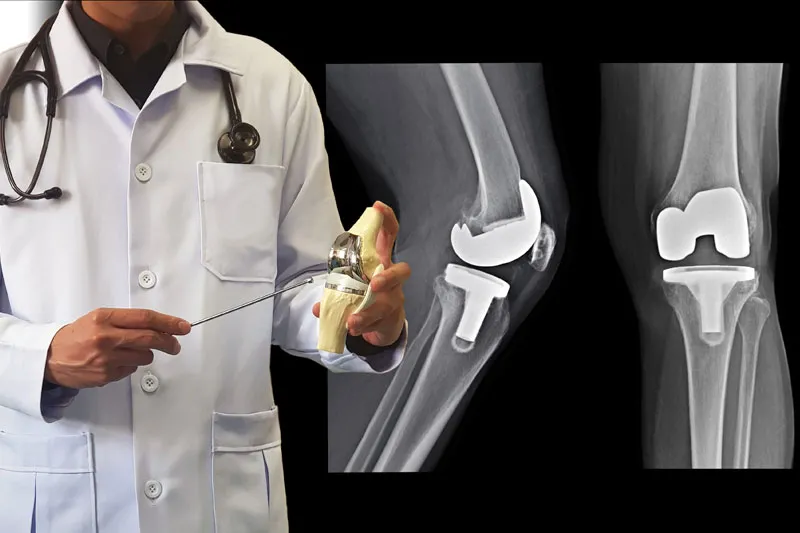
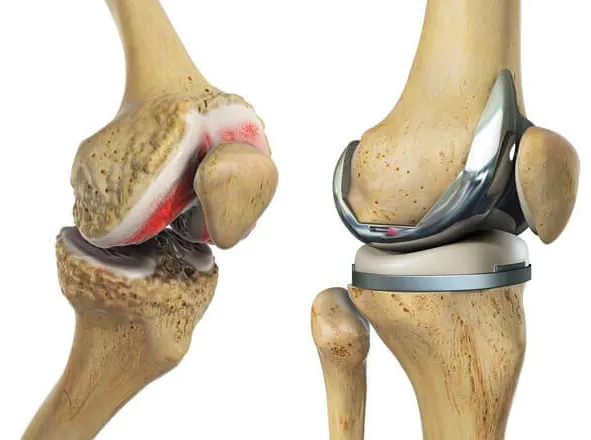
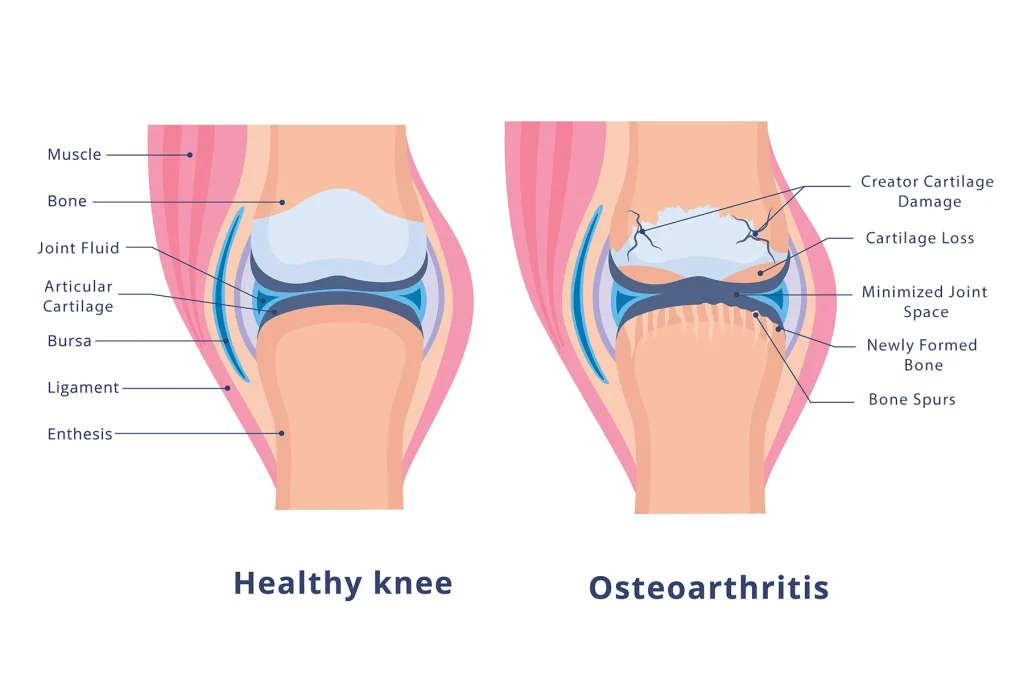
How We Work
Frequently Asked Questions about Bow Leg Correction
What does a bone gap mean?
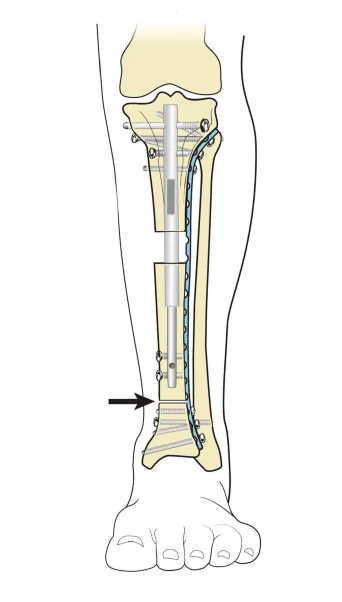
A bone gap (also called a bone defect) is a missing section of bone that prevents natural healing. It can occur after trauma, infection, or surgery when the bone tissue is lost. Unlike simple fractures, bone gaps usually need advanced surgical techniques like Ilizarov bone transport or bone grafting to restore continuity.
What causes a gap in the bones?
Bone gaps are most commonly caused by:
- Severe trauma (road accidents, gunshot wounds).
- Infections like osteomyelitis.
- Tumor removal surgery.
Failed fracture treatments (nonunion).
These conditions leave an empty space where the bone cannot heal naturally.
How to fill a bone gap?
Bone gaps can be filled by:
- Bone transport (Ilizarov technique) where new bone is gradually generated.
- Bone grafting (using the patient’s bone or donor bone).
- Vascularized bone transfer (like fibula graft).
Small gaps may sometimes heal with grafts, but larger ones require advanced reconstruction.
How big a gap can a bone heal on its own?
A small gap of 1–2 mm may heal naturally during fracture repair. Larger gaps (more than 1 cm) usually require surgical intervention because the bone cannot bridge the empty space on its own.
What is bone gap healing?
Bone gap healing refers to the process of regenerating new bone in an area where bone is missing. With modern techniques like the Ilizarov method, even large gaps of 10–15 cm can be reconstructed successfully.
How can I improve bone healing?
To improve bone healing:
- Eat a diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, protein, and zinc.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol.
- Follow your doctor’s physiotherapy plan.
- Take supplements if prescribed.
Bone healing goes through five stages: hematoma formation, soft callus, hard callus, consolidation, and remodeling.
What are the best foods for bone healing?
Foods that promote bone healing include:
- Dairy products: milk, curd, paneer (rich in calcium).
- Leafy greens: spinach, kale (calcium + vitamin K).
- Protein sources: eggs, chicken, fish, pulses.
- Nuts & seeds: almonds, sesame, chia seeds.
- Fruits: oranges, papaya (vitamin C for collagen).
Can cartilage grow back naturally?
Cartilage has very limited self-healing ability because it lacks a blood supply. Small defects may show minor repair, but significant cartilage damage usually requires medical or surgical treatment like microfracture surgery, stem cell therapy, or regenerative techniques.
Which medicine regenerates cartilage?
Currently, no oral medicine can fully regenerate cartilage. However, glucosamine, chondroitin, collagen peptides, and hyaluronic acid supplements may help slow cartilage damage and support joint health. Advanced therapies like PRP (platelet-rich plasma) and stem cells are being used in some cases.
Can diet help cartilage repair?
Yes, diet supports cartilage health. Foods rich in:
- Collagen & protein (bone broth, eggs, fish).
- Vitamin C (citrus fruits, berries).
- Omega-3 fatty acids (flaxseeds, fish).
- Anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric.
These may improve joint strength, though severe cartilage damage still requires medical treatment.
Is turmeric good for cartilage repair?
Turmeric (curcumin) has anti-inflammatory properties that reduce pain and swelling in arthritis. While it does not directly regenerate cartilage, it may protect cartilage from further damage and improve joint comfort when used as a supplement.
Can exercise help cartilage regeneration?
Yes. Low-impact exercises like walking, cycling, swimming, and physiotherapy improve blood flow, strengthen supporting muscles, and reduce joint stress. While exercise does not regrow cartilage, it helps maintain joint function and mobility in patients with cartilage loss.
Is walking good for knee cartilage?
Yes, moderate walking is beneficial. It strengthens muscles, maintains joint lubrication, and slows stiffness. However, excessive walking on damaged cartilage can worsen pain, so activity should be guided by a physiotherapist.
Is Ayurveda effective for knee cartilage regeneration?
Ayurveda offers herbal medicines, oils, and therapies for joint pain and inflammation. While it may provide symptom relief, there is no scientific evidence that Ayurveda can regenerate lost cartilage. Advanced cartilage loss still requires orthopedic treatment.
👉 Insurance coverage: Ayurvedic knee treatments are usually not covered by insurance unless provided in AYUSH-recognized hospitals.
What supplements grow cartilage?
Supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, collagen peptides, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids may help protect and support cartilage. They are not a cure but can slow degeneration and improve joint function.