How We Work
Frequently Asked Questions about Bow Leg Correction
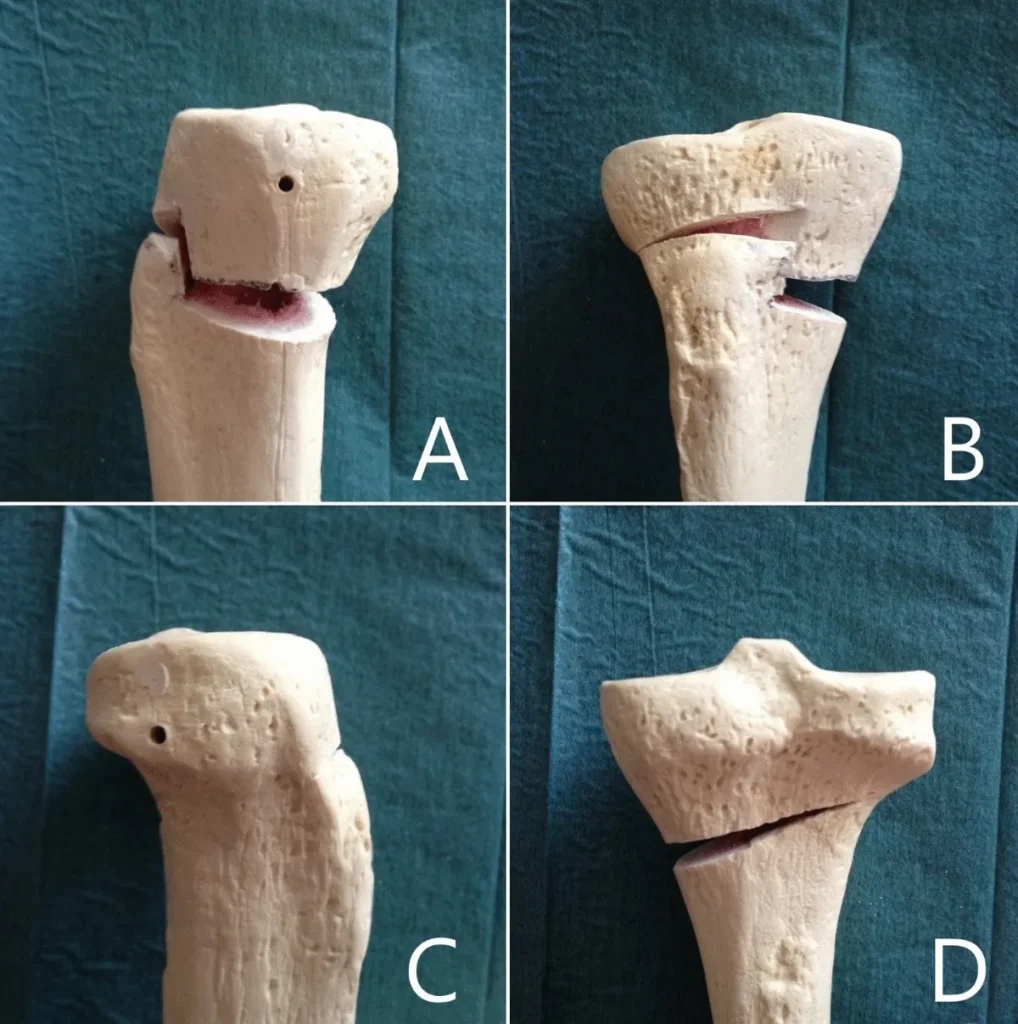
Is high tibial osteotomy major surgery?
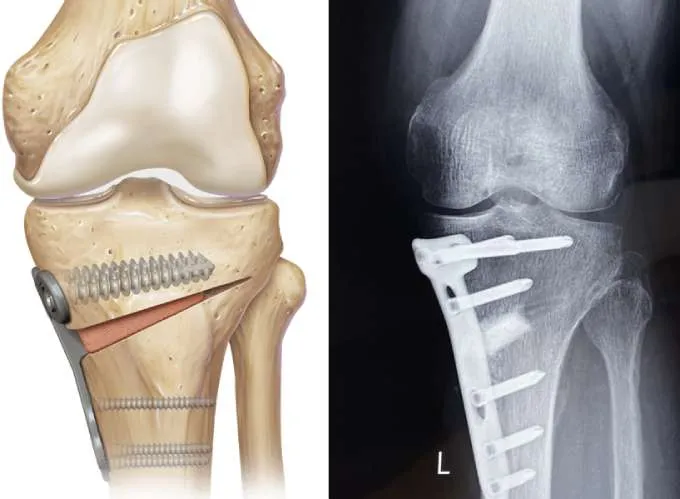
Yes, high tibial osteotomy (HTO) is considered a major orthopedic surgery because it involves cutting and realigning the tibia. However, it is less invasive than total knee replacement and aims to preserve your natural joint. With modern techniques and experienced surgeons like Dr. Divya Ahuja, the risks are minimized, and recovery outcomes are excellent.
What is the most common complication of high tibial osteotomy?
The most common complication is delayed bone healing or nonunion at the osteotomy site. Other possible issues include infection, stiffness, or irritation from plates and screws. Regular follow-ups and physiotherapy help reduce these risks.
How long does it take to recover from a high tibial osteotomy?
Most patients need 3–6 months to return to daily activities. Full recovery, including sports or high-impact activities, may take 6–12 months. Recovery depends on age, bone health, and physiotherapy participation.
How much does HTO surgery cost?
In India, especially Mumbai, HTO surgery costs around ₹2.5–4.5 lakhs depending on hospital, implants, and patient condition. It is significantly more affordable compared to Western countries, while maintaining high success rates.
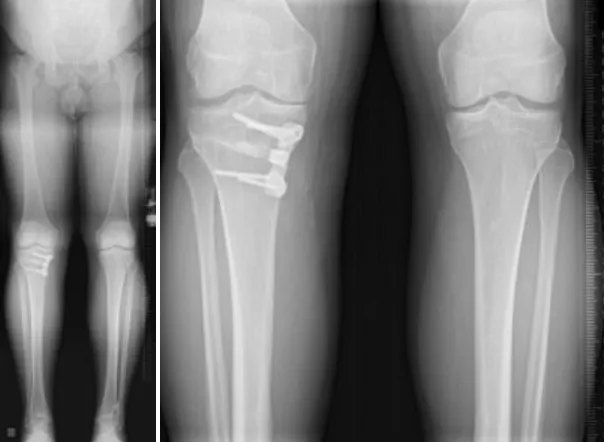
What is the ideal age for HTO surgery?
The ideal age is typically 40–60 years, when patients have early arthritis and good bone health. Younger patients with bow legs or deformities can also benefit. The key factor is the condition of the knee rather than age alone.
Can you walk after a high tibial osteotomy?
Yes. Patients usually begin partial weight-bearing with crutches within a few weeks. Full weight-bearing is gradually introduced as the bone heals, often by 6–8 weeks.
How successful is HTO surgery?
HTO has a success rate of over 85–90% in relieving pain and improving function. Results typically last 8–15 years, after which some patients may require a knee replacement.
How to sleep after a high tibial osteotomy?
Patients are advised to sleep on their back with the operated leg elevated on pillows to reduce swelling. Side sleeping may be possible after a few weeks, but only with proper support.
Which is better, knee replacement or osteotomy?
It depends on the patient. HTO is better for younger, active patients with early arthritis as it preserves the natural knee joint. Knee replacement is more suitable for older patients with advanced arthritis affecting the whole knee.
What is the aftercare for a high tibial osteotomy?
Aftercare includes wound care, physiotherapy, pain management, and avoiding high-impact activities during healing. Elevation, ice therapy, and regular follow-ups are also important.
Who is a good candidate for HTO?
Good candidates are younger or middle-aged patients with pain on one side of the knee, bow leg deformity, or early arthritis. Active lifestyle and good bone quality are important factors.
How long should I elevate my leg after tibia surgery?
Elevation is recommended for the first 2–3 weeks, especially after surgery, to reduce swelling and pain. Even after that, elevating the leg when resting helps with recovery.
Can you bend your knee after an osteotomy?
Yes, knee bending exercises usually start soon after surgery under physiotherapy guidance. Full bending may take several weeks to months, depending on healing progress.
How long does pain last after a high tibial osteotomy?
Pain is most significant in the first 1–2 weeks but improves steadily. Mild discomfort may last for a few months, especially during physiotherapy and walking.
What precautions should you take after tibia surgery?
Avoid putting full weight on the leg too soon, keep the wound clean, attend physiotherapy sessions, and take prescribed medications. Smoking and alcohol should be avoided as they slow bone healing.
What are the side effects of high tibial osteotomy?
Side effects may include swelling, temporary stiffness, pain, and in rare cases, infection or delayed healing. Most are manageable with proper care and monitoring.
What is a half-knee replacement called?
A half-knee replacement is called a unicompartmental knee replacement (UKR) or partial knee replacement. It replaces only the damaged portion of the knee, unlike HTO which preserves the natural joint.
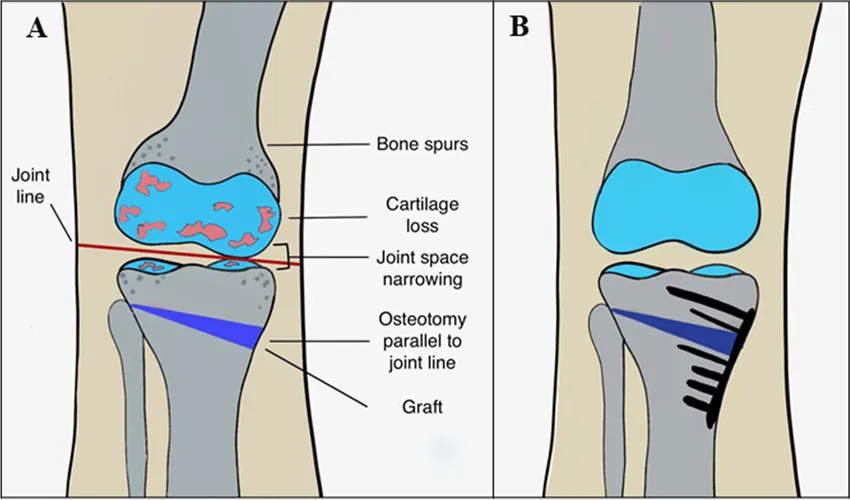
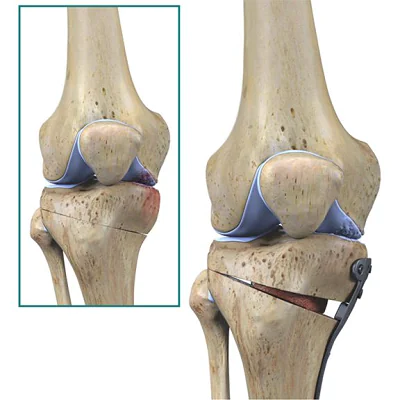
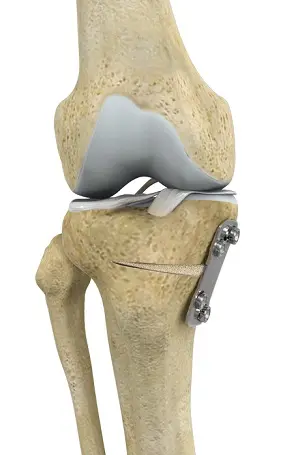
What is the purpose of HTO?
The main purpose is to realign the knee joint, shift body weight away from the arthritic side, relieve pain, and preserve the natural joint. It allows patients to stay active longer before considering knee replacement.
What is the difference between knee replacement and HTO?
- HTO: Realigns the tibia, preserves the knee joint, and delays arthritis progression.
- Knee Replacement: Replaces the entire joint surface with an artificial implant.
What is the disadvantage of osteotomy?
The main disadvantage is a longer recovery period compared to knee replacement. Also, some patients may still require a knee replacement later in life.
What kind of anesthesia is used for high tibial osteotomy?
HTO is usually performed under spinal or general anesthesia, depending on patient health and preference. Regional anesthesia with sedation is also commonly used.
How long to straighten a leg after knee surgery?
It may take 6–12 weeks of physiotherapy to fully straighten the knee after HTO. Early exercises and stretching are critical for regaining full motion.