How We Work
Frequently Asked Questions about Bow Leg Correction
What is a limb length discrepancy (LLD)?
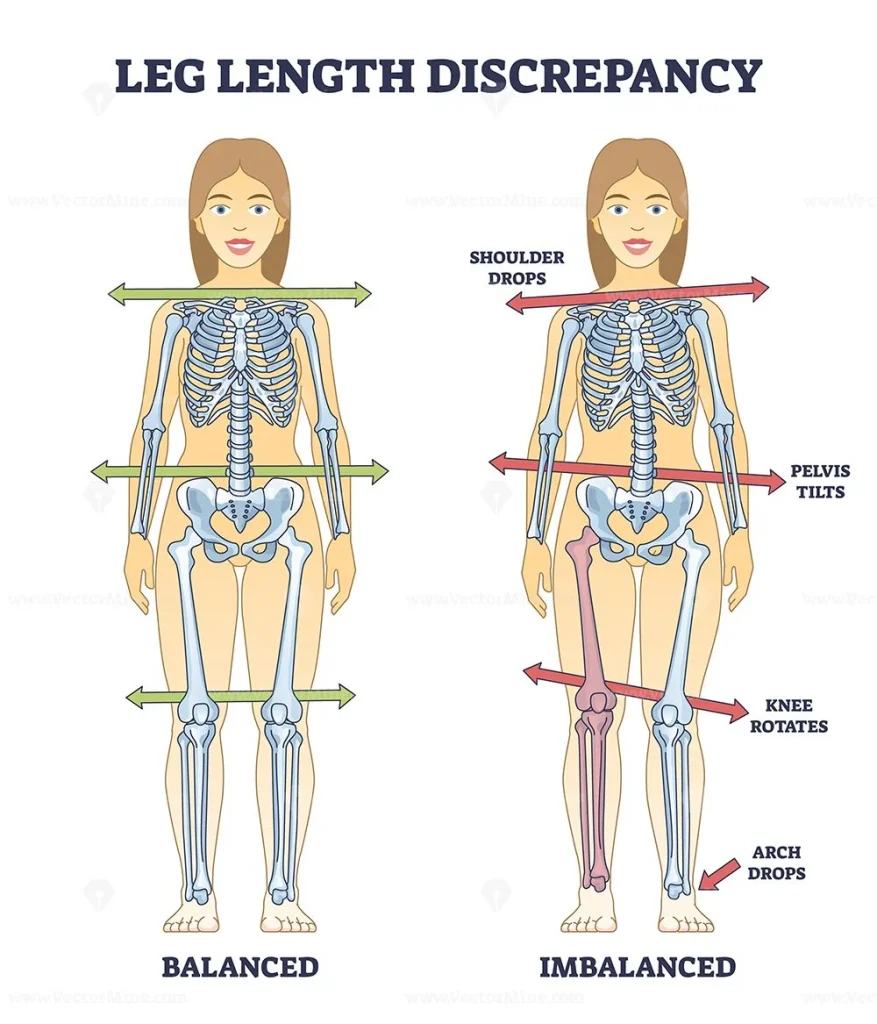
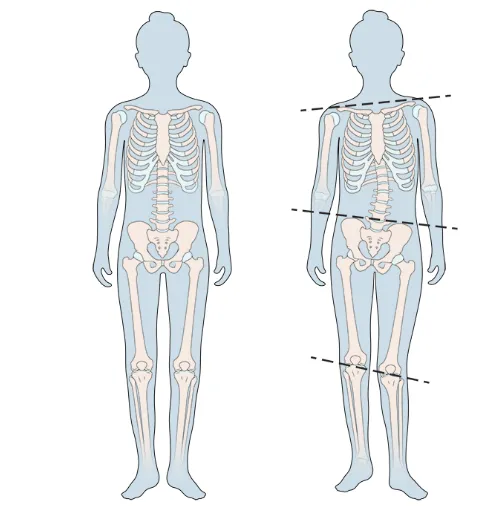
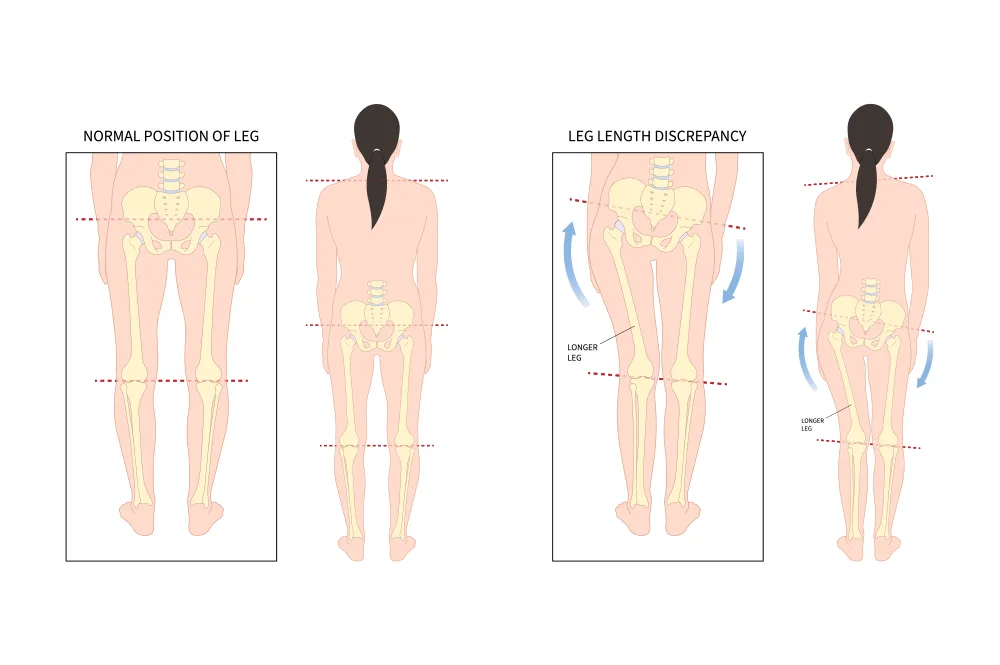
A limb length discrepancy (LLD) means one leg is shorter than the other. The difference can be small and harmless or large enough to cause walking problems, pain, and posture imbalance.
Should you correct a 0.5-inch leg discrepancy?
A difference of 0.5 inch (~1.2 cm) is usually minor and often doesn’t need surgery. Small discrepancies can be managed with shoe lifts or orthotics if they cause symptoms. Larger or painful differences may require medical correction.
What causes limb length discrepancy?
LLD can be congenital (present from birth) or acquired (develops later). Common causes include fractures, growth plate damage, infections, hip dysplasia, or past surgeries. Genetics may also play a role in some conditions.
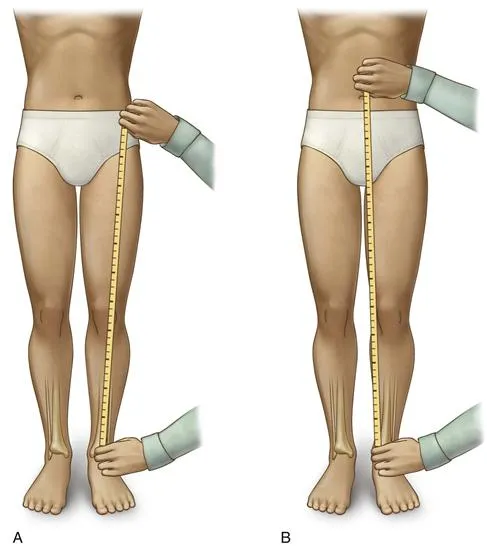
How is limb length discrepancy diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a clinical exam, where the doctor measures leg lengths. Imaging tests like X-rays, scanograms, or CT scans provide exact measurements and help plan treatment.
What is ILD disease? Is ILD a disability?
ILD usually refers to Interstitial Lung Disease, which is different from LLD. It is a chronic lung condition that can cause disability in advanced cases. It is not related to limb length discrepancy (LLD).
What happens if leg length discrepancy is left untreated?
Untreated LLD can cause chronic back pain, hip/knee arthritis, balance issues, and scoliosis (spinal curvature). Over time, it may also affect walking and limit sports or daily activities.
Can a chiropractor fix leg length discrepancy?
Chiropractors can help with functional discrepancies caused by muscle or posture imbalance. But for true structural discrepancies (actual bone length difference), only medical treatment like shoe lifts or surgery is effective.
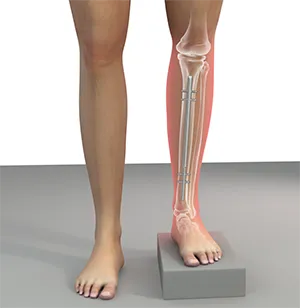
Can limb length discrepancy be cured?
Yes, most cases can be corrected. Small differences are managed with lifts, while larger ones can be cured using limb lengthening surgery (Ilizarov or PRECICE nails) or growth plate procedures in children.
How long does limb length discrepancy treatment take?
Treatment time depends on the size of the discrepancy. Shoe lifts work instantly, while surgical limb lengthening may take 6–12 months for full correction and recovery.
Does limb length discrepancy cause back pain and balance issues?
Yes. LLD often leads to spinal misalignment, back pain, hip strain, and balance problems. Uneven walking puts extra stress on muscles and joints, causing long-term discomfort if untreated.
Which hip hurts with leg length discrepancy?
Usually, the longer leg’s hip bears more stress and pain, but the shorter leg can also cause discomfort. Over time, both hips may develop strain due to uneven weight distribution.
What muscles are affected by limb length discrepancy?
LLD affects the hip flexors, hamstrings, gluteal muscles, and spinal stabilizers. These muscles work harder to compensate for imbalance, leading to stiffness and fatigue.
Can physical therapy or exercises fix leg length discrepancy?
Physical therapy cannot change bone length, but it helps manage symptoms. Strengthening, stretching, and posture exercises improve balance and reduce pain. Surgery or lifts may still be required for permanent correction.
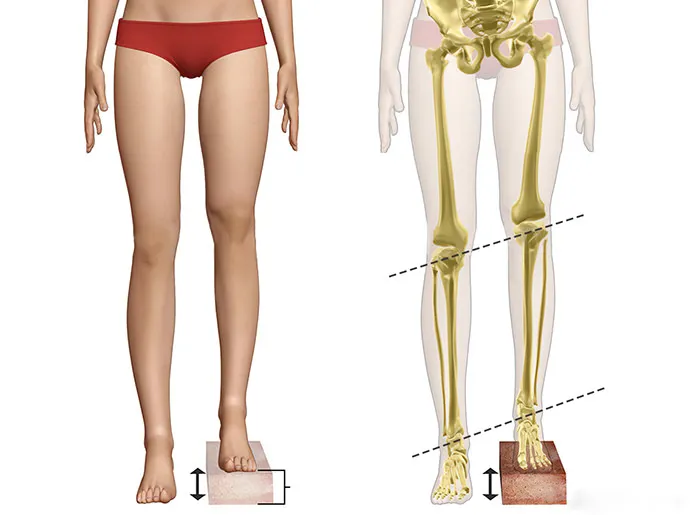
Can shoe inserts fix leg length differences?
Yes. Heel lifts or shoe inserts are effective for minor discrepancies (<2 cm). They help balance the legs, reduce pain, and improve walking.
Is leg length discrepancy genetic?
Some congenital cases have a genetic component, such as conditions affecting bone development. However, most discrepancies are due to injury, infection, or growth plate damage.
What exercises help with leg length discrepancy?
Exercises focus on core strengthening, hip and back stretches, balance training, and gait correction. While they don’t fix bone length, they improve posture and reduce discomfort.