Table of Contents
When patients face severe bone loss after accidents, infections, or surgery, doctors often consider two main options: bone grafts vs bone transport surgery. Both aim to restore missing bone and regain function, but they work in very different ways.
At Dr. Divya Ahuja’s Limb Reconstruction Clinic, the choice is always personalized, based on the patient’s age, the extent of bone loss, and their long-term goals. This article breaks down the key differences between bone grafts and bone transport, enabling patients and their families to make informed decisions.
Learn more about bone transport here: Bone Transport Surgery Explained
What Are Bone Grafts?
A bone graft is when bone tissue is taken from another part of your body (autograft), a donor (allograft), or a synthetic substitute and placed in the defect to help bones heal.
When Bone Grafts are used
- Small to medium-sized bone defects
- Fractures that aren’t healing properly (non-unions)
- To support spinal fusions or joint reconstruction
Advantages Of Bone Grafts
- Relatively short surgery and recovery time
- Works well for small defects
- Can be combined with fixation plates or screws
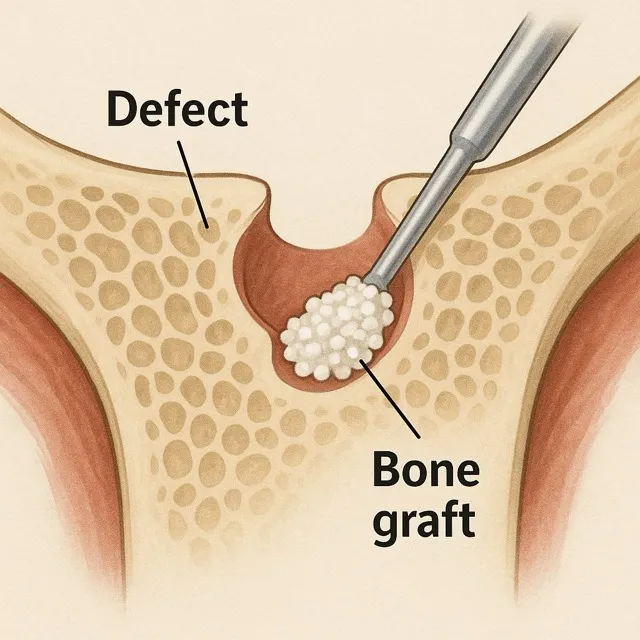
Limitations Of Bone Grafts
- Limited in large defects (more than 5–6 cm)
- Donor site pain (if own bone is used)
- Risk of graft not uniting or getting reabsorbed
- Cannot always fight an infection if present
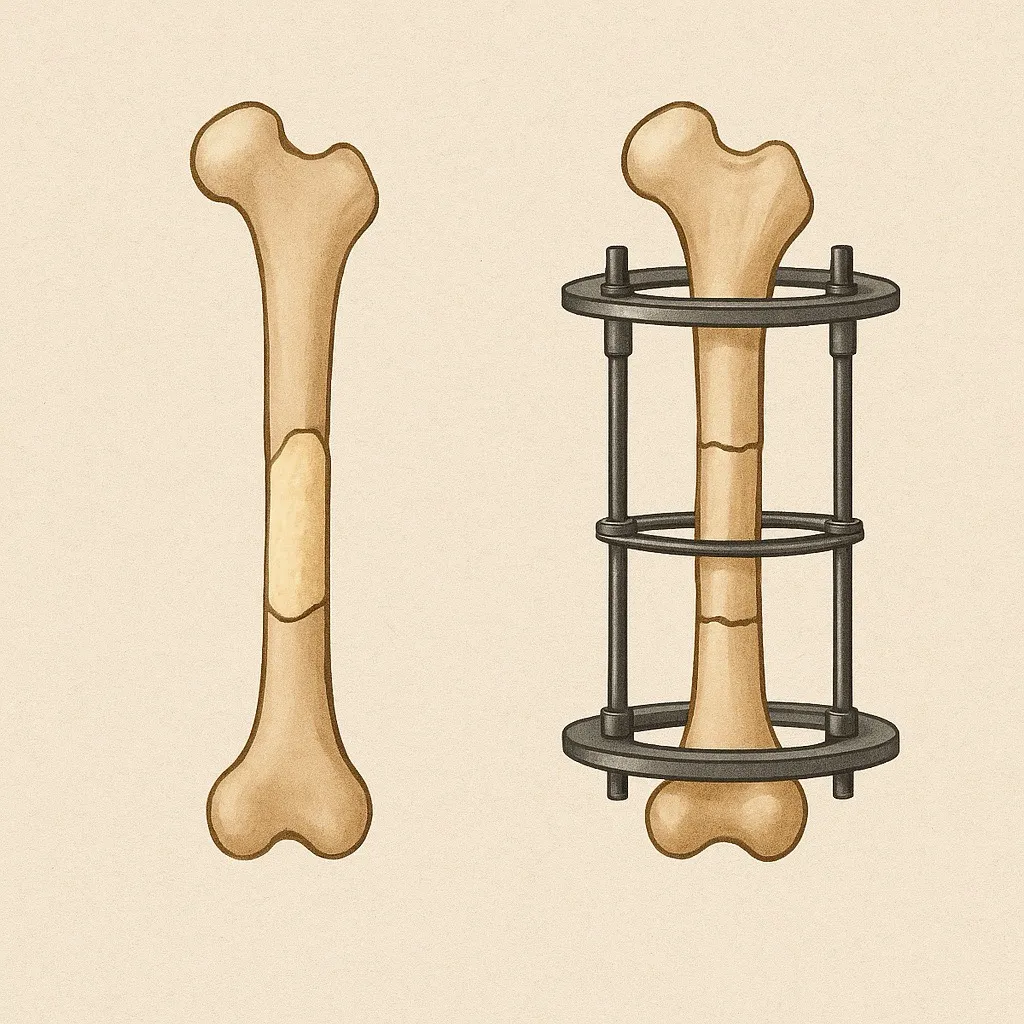
What is Bone Transport Surgery?
Bone transport uses an external fixator device (like an Ilizarov frame) to regenerate new bone slowly. Healthy bone is cut and gradually moved across the gap, while new bone forms behind it.
When is Bone Transport Surgery Used
- Large bone defects after trauma
- Bone infections (osteomyelitis)
- Failed bone grafts or repeated surgeries
- Length discrepancies and deformity corrections
Advantages of Bone Transport Surgery
- Can reconstruct very large bone defects (even >10 cm)
- Uses the body’s natural healing power
- Avoids the need for large donor grafts
- Can simultaneously correct deformity and infection
Limitations Of Bone Transport Surgery
- Requires patience: treatment takes months
- Daily fixator adjustments
- Pin-site infections are possible (but manageable)
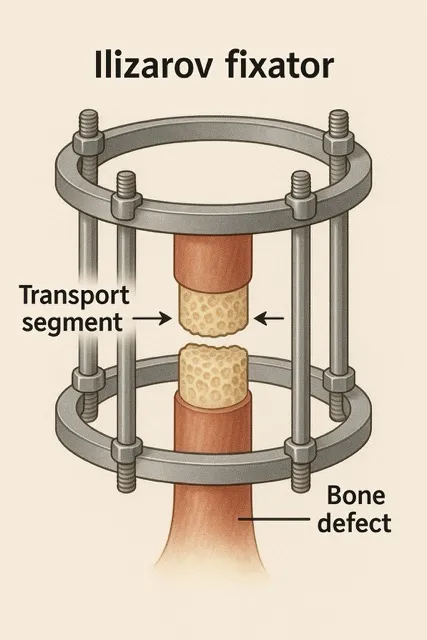
Bone Grafts vs Bone Transport: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Factor | Bone Graft | Bone Transport |
| Best for | Small to medium bone defects | Large or complex bone defects |
| Source | Autograft, allograft, or synthetic | Patient’s own bone regeneration |
| Surgery type | Single procedure | External fixator + gradual process |
| Healing time | Weeks to months | Months to a year (depending on defect) |
| Infection control | Limited | Very effective (can treat chronic infections) |
| Long-term strength | May weaken if graft fails | Strong, biologically natural bone |
How Doctors Decide Between Bone Graft and Bone Transport
- Defect size: Small → graft, Large → transport
- Presence of infection: Transport preferred if infection exists
- Patient age & health: Younger patients heal faster, making transport ideal
- Previous surgeries: Failed grafts may need transplant surgery
Dr. Divya Ahuja’s Expertise
Dr. Ahuja has extensive experience in both bone grafting and advanced bone transport techniques using Ilizarov and modern fixators. His patient-first approach guarantees the selection of the least invasive yet most effective treatment for each case.
Why Parents Trust Him
- Specialist in Bone Transport Surgery and reconstructive orthopedics
- Over 15 years of surgical experience
- Focused on minimally invasive and friendly care
- Explains procedures in simple terms, guiding parents every step of the way
Patient-Centric Care
Dr. Ahuja combines precision surgical planning with a warm, approachable manner—helping families feel reassured at every stage.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Path
Both bone grafts and bone transport surgery have a place in modern orthopedic treatment. The right choice depends on the size of the defect, the presence of infection, and overall patient health.
At Dr. Divya Ahuja’s clinic in Mumbai and Navi Mumbai, patients receive personalized treatment plans, whether that means a simple graft or advanced bone transport with Ilizarov techniques.
Clinical Locations of Dr. Divya Ahuja
Our Clinical Locations
Tap a location to view timings, contact, and map.
Broadway Healthcare, Dadar East
Broadway Healthcare, Dadar East
Clinic Info
- 📍 Broadway Healthcare, Dadar East, Mumbai
- 🕒 Wednesdays · 10:00 AM – 12:00 NOON
- 📞 Appointments: +91 93213 17227
Sweet Clinics, Vashi, Navi Mumbai
Sweet Clinics, Vashi, Navi Mumbai
Clinic Info
- 📍 Sweet Clinics, Vashi, Navi Mumbai
- 🕒 Fridays · 10:00 AM – 12:00 NOON
- 📞 Appointments: +91 93213 17227
Heal Well Speciality Clinic, Thane West
Heal Well Speciality Clinic, Thane West
Clinic & OPD Info
- 📍 Heal Well Speciality Clinic, Thane West
- 🕒 Every Wednesday 10:00 AM – 11:00 AM
- 📞 Appointments: +91 81691 04438
Mangal Anand Hospital, Chembur Mumbai
Mangal Anand Hospital, Chembur Mumbai
Clinic & OPD Info
- 📍 Mangal Anand Hospital, Chembur Mumbai
- 🕒 Monday, Wednesday, Friday 03-07 PM, Thursday 06-07 PM, Free OPD Saturday 02-04 PM
- 📞 Appointments: +91 70212 18182
SRV Hospitals, Tilaknagar, Chembur
SRV Hospitals, Tilaknagar, Chembur
Clinic Info
- 📍 SRV Hospitals, Tilaknagar, Chembur
- 🕒 Monday, Wednesday, Friday 11 AM-12 PM
- 📞 Appointments: +91 84518 00800
FAQs
Which surgery is less painful?
Bone grafting is usually shorter and less invasive, with pain mainly from the donor site if your own bone is used. Bone transport involves wearing an external fixator for months, which can cause some discomfort, especially during daily adjustments. However, with proper pain management, both procedures are well tolerated.
Is bone transport better than grafting?
Bone transport is usually preferred for large or infected bone defects, while grafting is better for small gaps. Transport creates new bone naturally, while grafts “fill” the defect. Neither is always better—the right choice depends on the patient’s condition.
Can both be combined?
Yes, in complex cases, surgeons may combine both. Bone transport can cover most of the gap, and a small graft may be used to strengthen the final section. This hybrid approach can shorten treatment time and improve outcomes.
How long do external fixators stay for bone transport?
The fixator stays until the new bone is fully formed and strong. This usually takes several months, depending on the defect size. For example, a 6 cm gap may need around 6–8 months for transport and consolidation.
Which option is more successful in the long run?
Bone transport generally has higher success for large, complex cases because it uses the body’s own biology to regenerate bone. Grafts work well for smaller defects but may fail if the gap is too large or if infection is present.
What is the recovery time for bone grafts vs bone transport?
Bone graft patients usually recover in a few weeks to months. Bone transport takes longer—often 6–12 months—since new bone has to grow and harden.
Can children undergo bone transport surgery?
Yes. In fact, bone transport works very well in children because their bones heal and regenerate faster than adults.
Is bone transport surgery permanent?
Yes. Once the new bone has fully healed and consolidated, it is as strong as natural bone and usually does not require further surgeries.
Are there risks of failure in bone grafts and transport?
Both procedures have risks, such as infection or delayed healing. Grafts may fail to unite in large gaps, while transport may have issues like pin-site infections. With expert care, most problems are manageable.
How do I know which treatment I need?
The decision depends on the size of the defect, the presence of infection, age, and overall health. Small defects are usually treated with grafts, while larger or infected gaps are better suited for bone transport.